Graves: Steps to explain the behavior of managers.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is often used to explain the motivation and thus essential behavior patterns of employees. Maslow’s theory assumes that human beings do not only respond to outside stimulation, but quest for self-realization. According to this theory human can evolve only if specific needs are satisfied. Motives are divided into five classes that build on one another and represent groups of needs. Only when the motive below is satisfied the next higher one can be activated. Often Maslow’s model is criticized as a too general approach in consideration of multiple different needs. The end point of Maslow’s pyramid is also the end of human development, which is rated as too narrow and inflexible.
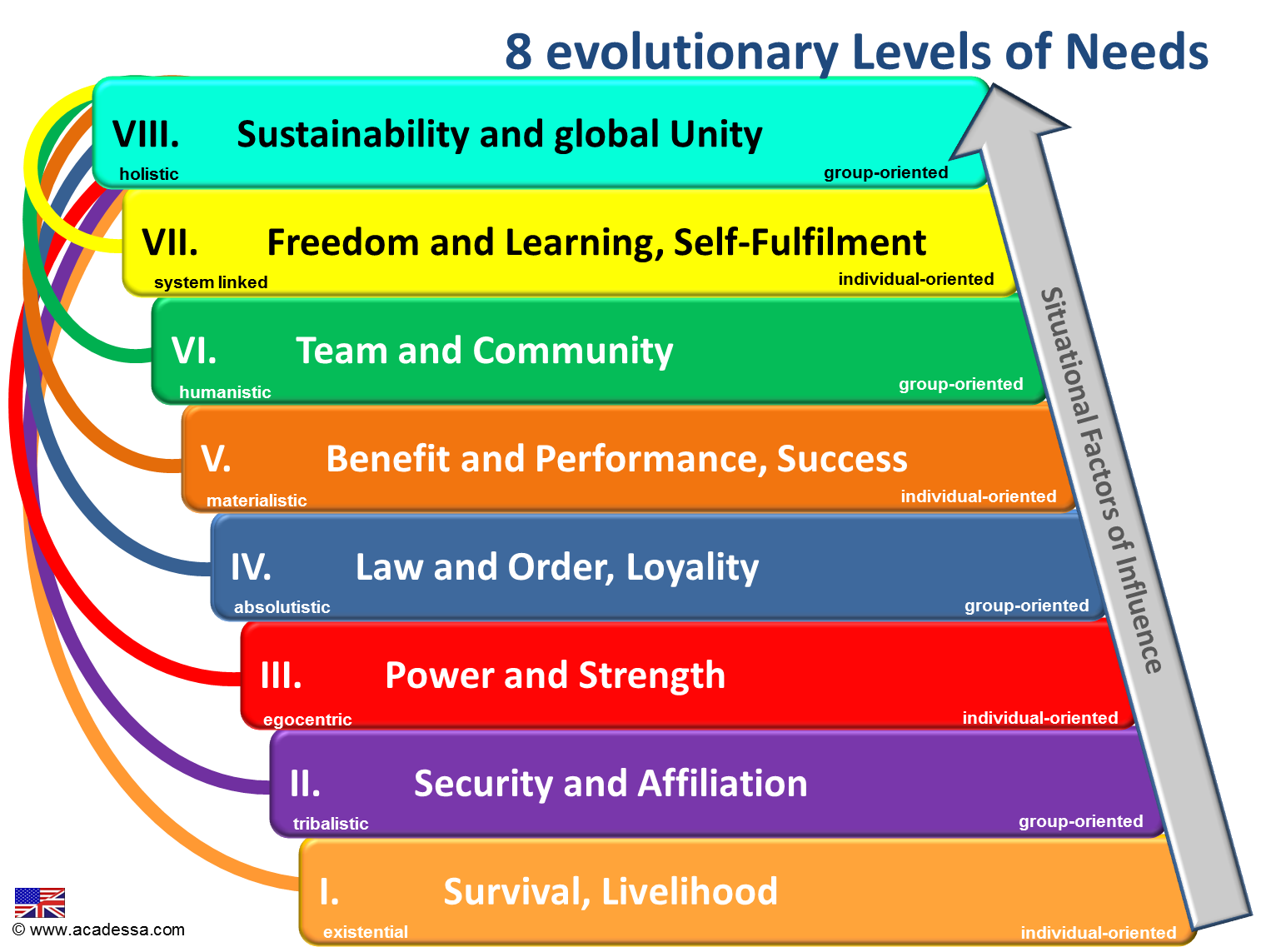
Claire W. Graves follows the existing criticism on Maslow’s model and develops a much more sophisticated model. It is referred to as „Emergent Cyclic Levels of Existence Theory“ or simply as Graves‘ value system. Graves came to the conclusion that the top three needs are satisfied in different ways, depending on the value system of a person and his social environment. According to Graves‘ development model of organizations and individuals certain value systems have evolved in response to the human conditions of existence. His value system is divided into eight levels that build evolutionary on each other and are non-hierarchical: The development to the next level is not linear, but due to many different influences in a way spiral. Graves’ model provides insights into the motivational structure of individuals. It creates a view on the influence of changing situational factors on the development of people organizations.
In every single evolutionary level of the model there is one specific type within the community that represents a specific need or motive associated with a value proposition. The needs are divided into eight value systems, alternating individual- oriented and group-oriented values classes.
The model provides a good base to explain the motivation of managers and thus a substantial part of their behavior in organizations. It is a helpful starting point to create hypotheses why some managers are successful and others fail.