The term „digital transformation“ is a buzzword that is used and abused with multiple meanings. Since 2005 the usage of digital technologies and its potentials have changed markets and industries fundamentally, especially as these technologies give users the choice how to satisfy specific needs. Some call this the „digital revolution“ according to a Kondratiev wave analog to the industrial revolution in the late 18th and 19th century. Digital transformation refers to these changes with a modification of companies‘ existing technologies and business models. Digital transformation is based on people, processes and technologies and is relevant for any company that offers services or products online.
You can split digital transformation in four different dimensions that can apply parallel, shifted or sequential: product transformation, company transformation, industry transformation and society transformation (see Figure 1). Product transformation can be internal related to a companie’s products and services or external related to a specific product category.
Why is digital transformation so important?
Digital transformation should be part of any digital strategy. Clearly spoken, a company without any digital strategy has no future strategy and risk its existence. If companies miss to transform their strategy into digital and leave the market you can call it „digital Darwinism„.
According to a Gartner study in 2020 there will be more than 25 billion connected „things“ such as devices, cars, homes and wearables. So who will buy unconnected things in the future if nearly everything will be connected? Also in 2020 about 80% of revenues will be related to additional services and only 20% to the core product itself, similar as we know it already from existing app and widget ecosystems.
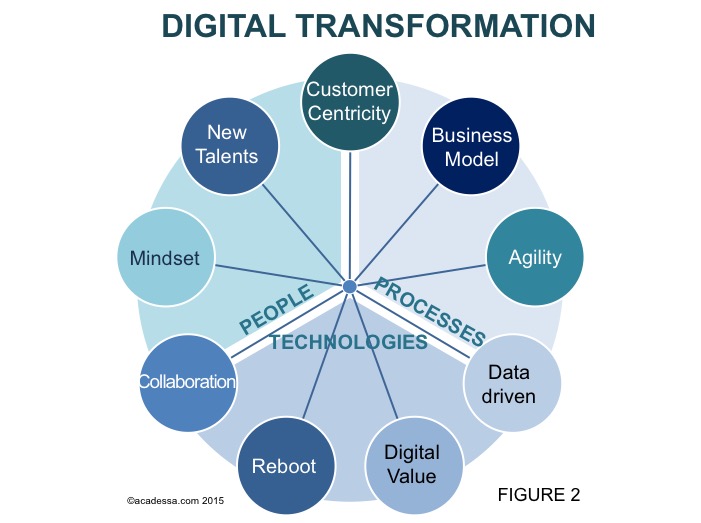
I collected nine pillars that could help companies to prepare and drive digital transformation in their organization (see Figure 2).
1. Mindset of Change
To be able to transform existing and established models you need to install a „mindset of change“. This is not only related to technologies or development, but to whole organization. It should start with an impulse on top management level driven top-down and parallel in specific teams driven sideways and bottom-up. Specific teams means groups that are more open to change and that are less hierarchical organized anyway. Change is often creating resistance as some employees might understand it as a threat for status, role or even their job. It will take time, patience and some distinguished supporters to Establish such a different mindset. Mostly it makes sense to start in one department creating first positive signals of change.
2. New Talents
It is impossible to get everybody convinced and there are often also new skill sets required to transform products, services and organizations. Beside an investment in employees‘ training and coaching you need some new talents that already have some of the necessary new or modified skills to support the process of change. It is very important to have the HR team committed and involved in the whole initiative from the very first beginning.
3. Customer Centricity
The idea to put users of a product or service in the center of concept and development is not new at all. Many product managers might say: „We already do this for years“. But such an approach needs an organizational form and the understanding of all involved teams that is based on a continuous user dialog. There are multiple methods how to discover what are the most important user needs and what creates user stickiness. All these methods are based on iterative testing and adaption according to user input/feedback and created (digital) value. Customer integration is a clear commitment to focus on existing and future needs of users and supports the process to discover successful disruptive innovation.
4. Business Model
Does the current business model still fit to the existing demand and customer needs? Is there any growth in users and revenues? Are there any new technologies on the horizon that could change user behavior and demand?
A good example is how the way people buy and consume music has changed in the last 20 years. First CD sales shifted from offline stores to online shops in the late 90s, than people started to download music. As there was no common infrastructure and no simple standardized solution in place to buy and download music online, many users shared songs online for free illegally. The music industry tried to protect the existing business model instead of innovating and transforming. Apple’s iTunes was the breakthrough for legal paid music downloads. Currently users switch to subscription based music streaming services such as Apple Music or Spotify. The music CD is already dead and music downloads are riding into sunset.
It is always tough to change existing business models and revenue streams as long as they seem to work „somehow“. It is even more difficult, if the change requires a modification of an established value chain. That is why companies from other industries or even small startups often step successfully into existing markets with a different or totally new approach.
In 2014 Airbnb, a marketplace for renting lodgings founded in 2012, sold more accommodations as the whole Hilton Group, founded in 1919.
5. Agility
Agile concepts are a common toolkit to drive change and serve as a framework for customer centricity. Scrum is an agile framework for software development based on empirical process control by transparency, inspection and adaption. Many of Scrum’s agile principles can be used outside of software development in any department or project. These are cross-functional collaboration in teams, self-organization inside the teams, a prioritization based on (digital) value and an iterative realization process instead of a static long term planning. Agility means for companies and teams also the acceptance to make mistakes and to understand those as a part of their leaning process.
6. Data driven Business
This pilar adds data to the commitment for customer centricity. Any new product idea, feature or potentially improvement of a product or service can be tested with users. There are multiple methods to validate ideas, concepts or prototypes with users or even to discover and create a best-practice option in collaboration with users. Such an approach reduces the risk to fail with an idea or product as the design is based on „measured“ existing or future needs of real users.
General speaking, data does not only help to save money, it is money. Data is a key driver of the mentioned digital revolution. The succes of some of today’s most valuable companies such as Apple, Google (Alphabet), Microsoft, Facebook and Amazon is build on data. These companies produce, collect and analyze data to make decisions and to create (digital) value for their users and their company.
7. Digital Value
Digital value is the validated positive outcome of data driven decisions. Any prioritization of functionality and features has to be driven by its digital value. Digital value means an online driven, measurable direct impact for a company’s value chain such as business value (e.g. direct or indirect monetarization) or user experience value (e.g. engagement) or internal process value (e.g. huge improvements of the velocity of specific tasks). The value is created because a specific new user need was satisfied or an already existing user need was satisfied better or more efficient than before.
8. Reboot Technology
This pilar refers to the fact that digital transformation often includes something radical and disruptive that mostly cannot be realized based on implemented and established technology. How would you build a technology set-up for your company if you could start from scratch today? What is the key difference in such an approach and what is the key USP compared to existing competitors today? The idea of „re-coding“ sounds expensive, but can help to identify the most weak parts in the current technology. Today, a main requirement to software architecture is changebility what means a modular lean structure is preferred over monolithic „all-in-one“ solutions we know from the past. That does not include a kind of total technological flexibility what could be much too complex and expensive. Modularity means to create a core and to build modules around it, to use APIs and also 3rd party modules. The microservice architecture follows these paradigms. Not every feature or service has to be developed from an internal team, especially if there are standard solutions already available on the market, that could be integrated in such a modular architecture.
Simplicity is a second requirement for technology. This could be rated as inconsistent with the requirement of changbility, but it is not. Only a good balance between both is necessary.
9. Collaboration
Collaboration is the connector between mindset of change, customer centricity, agility and digital value and the enabler of a successful digital transformation. Somehow collaboration is a consequence if a companie’s change strategy is supported by the main operative stake holders in key departments. Collaboration inside the company means also to share responsibilities and to work in cross-functional teams. You need to build expert teams with the most skilled people to solve a specific task or create a specific solution, independent from boundaries of departments. Boundaries of departments should be understood as lines, not walls.
Collaboration means also to integrate external partners, suppliers and users to creat the best possible solution. There are many examples of a successful user integration into companies‘ innovation process or even of product innovation communities, stimulating user driven innovations for specific brands or products.
How long is the process of digital transformation?
The time frame of a digital transformation is depending on the specific existing business and the size of the company. It seems more that digital transformation is tending to be a permanent process that is morphing from one wave to the next.

At the DigIT Conference in Berlin 2015 Heiko Meyer, Managing Director HP Germany, has explained the 5 years plan of HP’s digital transformation journey. Also after 5 years the real journey will rather start than end. Axel Springer SE, a traditional German publisher, has started its digitalization in 2006. In the first half of 2015 more than 60% of revenues are related to digital business models. The whole process was and still is digital transformation. Also companies that have alreday a 100% digital business model need to transform to the next digital level as markets and user requirements are evolving. So digital transformation is only a first step of a continuous change process that could be better described as digital evolution.